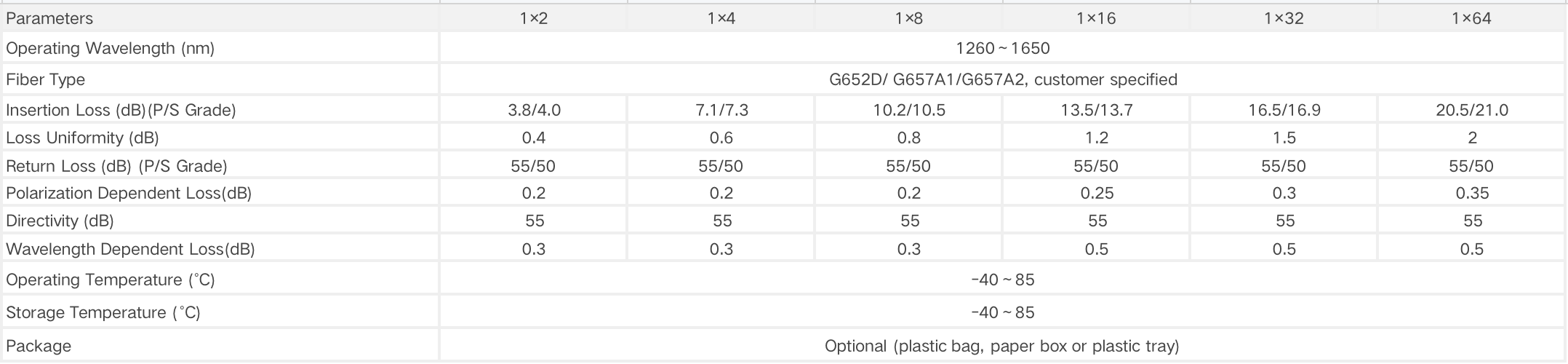
Input Channel Number: 1/2
Splitting Ratio: Equal or unequal splitter ratios
One or two inputs with an output maximum of 32 fibers.
Widely used in split configurations that are no more than 1×4
Connector: no connector / FC / SC / LC / or other type
Operating Wavelength:850nm, 1310nm, 1550nm
Operation Temperature: -5 to 75℃
The FBT Coupler, also known as the fused biconical taper splitter or FBT coupler, is a type of fiber optic splitter that appears similar to the bare PLC splitter and mini steel tube PLC splitter. The FBT splitter uses traditional technology to weld several fibers together from the side of the fiber. To align the fibers, they are heated at a specific location and length. Due to their fragility, the fused fibers are protected by a glass tube made of epoxy and silica powder. The inner glass tube is then covered by a stainless steel tube and sealed with silicon. Over time, the quality of FBT fiber splitter has improved, making them a cost-effective solution for deployment. FBT couplers are widely used in passive optical networks, particularly in split configurations that are no more than 1×4.
Features of FTB splitter
Order Information
Step 1: Consider the costs, performances & applications, and environments, choose which type of fiber optic splitter you’ll need, there are generally two types of fiber optic splitters: FTB Coupler and PLC Splitter.
FBT coupler is a fiber optic splitter made by fusing and stretching two or more optical fibers together to create a tapered region that splits and distributes the input signal between output fibers. FBT couplers are commonly used in fiber optic networks, but they have some limitations such as limited bandwidth and higher insertion loss.

PLC Splitter is highly preferred over the FBT splitter due to its numerous advantages such as its flexibility in working wavelength, high stability, low-temperature loss, and reduced failure rate. In recent times, PLC splitters are compact and can be integrated into small packages, making them ideal for use in optical communication systems where space is limited. There are several types of PLC (Planar Lightwave Circuit) splitters, which differ in terms of their design and functionality.
The difference between FTB Coupler and PLC Splitter
| Parameters | FBT Coupler | PLC Splitter |
| Operating Wavelength | 850nm, 1310nm, 1550nm | 1260nm -1650nm (full wavelength) |
| Application | CATV Systems, PON, FTTx Networks, etc. | CATV Network Systems, PON, FTTx Networks, etc. |
| Performance | 1×8 (can be larger with a high failure rate) | 1×64 (equal to all branches providing high reliability) |
| Branches Split Attenuation | Equal or unequal division, customized | Equal splitter ratios(non-customized) |
| Input/Output | One or two inputs with an output maximum of 32 fibers. | One or two inputs with an output maximum of 64 fibers. |
| Operation Temperature | -5 to 75℃ | -40 to 85 ℃ |
| Price | Lower | Higher than FBT Coupler |
| Summary | Used for simple signal splitting | Used for more complex and precise signal splitting in higher-capacity communication systems |

Bare fiber PLC Splitter

Micro PLC Splitter

ABS Box PLC Splitter

LGX Box PLC Splitter

Rack Mount PLC Splitter
Specification of PLC Splitter
1xN PLC Splitter
2xN PLC Splitter

Step 2: Choose the right fiber type, The splitter should be compatible with the fiber type you are using, whether it is single-mode or multimode.
Step 3: Decide which Splitting Ratio you’ll need in your network: The splitting ratio determines how many outputs are needed per input. Common splitting ratios include 1:2, 1:4, 1:8, 1:16, 1:32, etc. Make sure to choose the appropriate splitting ratio based on your specific needs.
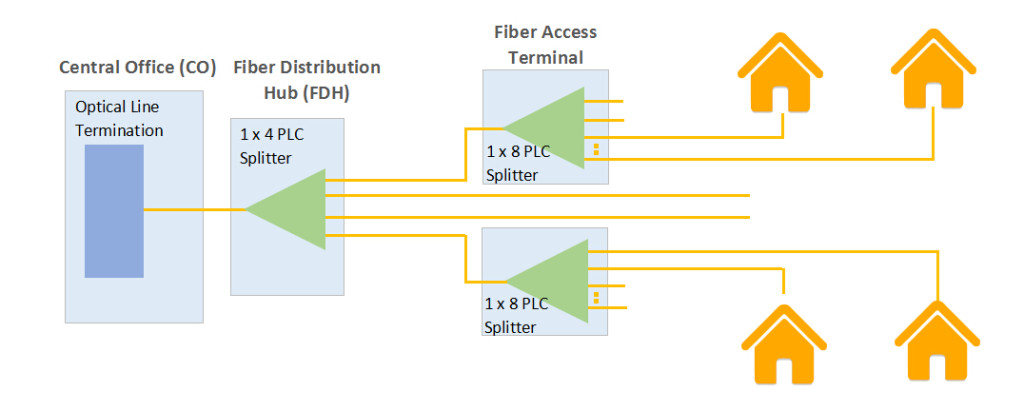
Step 4: Determine how many ports you require. Splitters are available in various configurations, ranging from one input and two outputs to one input and 64 outputs or more.
Step 5: Select the input and Output Connectors, the most common connector types are SC, LC, and FC.



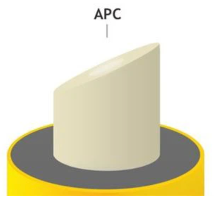
Step 6: Choose the polish type of connectors. There are two types of connector polish, UPC and APC.

Easy shop
Professional Seller
Excellent Quality
Global Shipping
Fast Delivery
We will contact you within 1 working day, please pay attention to the email with the suffix “@isp-home.com”.